Campaign: Improve maternal health
| Goal 5 of the UNs Millennium Development Goals is to REDUCE MATERNAL MORTALITY and IMPROVE MATERNAL HEALTH (Ref: UN MDG-5) |
Target 5A: Reduce by three quarters the maternal mortality ratio. (Reduce urban – rural/ developing – developed nations’ gap)
Target 5B: Achieve universal access to reproductive health (Antinatal care, family planning)
- For too many women across the globe, motherhood is far from being a fulfilling experience. It is associated with suffering, ill health and even death due to issues related to maternal health.
- When a mother dies, children lose their primary caregiver, communities are denied her paid and unpaid labour and countries forego her contributions to economic and social development.

Some facts:
- India has the largest number of births per year (27 million) in the world. Hence, India’s progress in reducing maternal deaths is crucial to the global achievement of MDG 5. India has a target of reducing maternal deaths to 109 by 2015. (Ref: WHO)
- However India, in spite of the economic progress the situation is grim. One woman dies during child birth every eight minutes (19% of global maternal deaths) and thus the nation has a long way to go before the UN target is achieved. (Ref: Huffington Post)

Source: Special bulletin on maternal mortality in India 2007 – 2009, Sample registration system, Office of registrar general, India. 2011
(http://www.censusindia.gov.in/vital_statistics/SRS_Bulletins/Final-MMR%20Bulletin-2007-09_070711.pdf )
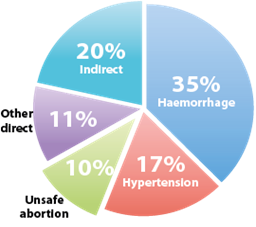
| Major direct causes of maternal mortality |
- Major causes of direct maternal mortality are:
- Haemorrhage
- According to a WHO review (Survey 1993 to 2005),
- 42% of pregnant women worldwide have anaemia which can significantly increase instances of maternal mortality due to heavy bleeding during childbirth;
- about 50 % of maternal deaths occur because of haemorrhage and sepsis.
- According to a WHO review (Survey 1993 to 2005),
- High blood pressure (Hypertension- Eclampsia)
- Pre-eclampsia is a hypertensive disorder characterized by the presence of high-blood pressure and high protein levels in the urine (proteinuria) during pregnancy. The disorder can develop in healthy women bearing their first child and can happen as early as 20 weeks of gestation. Delayed diagnosis can fatally affect maternal health. (Ref : Times of India, Dec 2011)
- Indirect causes include not having access to safety and benefits of institutional deliveries in India.
- Pre-eclampsia is a hypertensive disorder characterized by the presence of high-blood pressure and high protein levels in the urine (proteinuria) during pregnancy. The disorder can develop in healthy women bearing their first child and can happen as early as 20 weeks of gestation. Delayed diagnosis can fatally affect maternal health. (Ref : Times of India, Dec 2011)
- Haemorrhage
| Major barriers to reproductive health |
- Malnutrition and anaemia (Ref: Lancet online)
- For every woman dying during childbirth many more suffer- There are long-lasting and debilitating illnesses. 36% women malnourished, ~ 55 percent are anemic. Maternal under nutrition (body-mass index of less than 18.5 kg/m 2) is a life cycle issue that can result into short stature and low body-mass index affecting pregnancy and lactation.
- Mineral / Vitamin deficiencies are major issues. Iron deficiency is the most common form of malnutrition resulting into anaemia.
- Anaemia:
- According to a WHO review (Survey 1993 to 2005) 42% of pregnant women worldwide have anaemia.
- 75- 60% due to iron deficiency in non-malaria areas and 50% in malaria areas. (Anaemia could also be due to parasitic infections like Malaria).
- Anaemia can significantly increase instances of maternal mortality due to heavy bleeding during child birth
- Vitamin A deficiency
- Either due to inadequate intake or infection can lead to complications like still birth, low birth weight apart from affecting vision.
- Zinc deficiency
- Result into complications like prolonged labor, preterm delivery.
- Vitamin A and zinc deficiencies have by far the largest remaining disease burden among the micronutrients
- Iodine deficiency
- Even mild, subclinical maternal iodine deficiency during pregnancy impairs motor and mental development of the fetus and increases risk of miscarriage and fetal growth restriction

- Socio – cultural determinants
- Problem of exclusion (Ref: WHO):
- The available data suggest that the marginalized sections of the society suffer from a 'social gap' in terms of health status and health services.
- There have been attempts like Janani Suraksha Yojana by government of India. However the positive policy orientation (in terms of a comprehensive and joined-up vision) has not percolated into the implementation levels. (Ref: MoHFW-GoI)
- Mobilization of women using the group approach as witnessed in Kerala could be an answer for promoting equity and further improvements in maternal health
- Early age of marriage and Adolescent Mothers:
- Percent of girls marrying before the age of 18 is as high as 48% in poor population of India (the number is 29% for relatively affluent household).(Ref: TelegraphIndia)
- Adolescents age 15 through 19 are twice as likely to die during pregnancy or child birth as those over age 20. (Ref: AdvocatesForYouth)
- Gender inequity (compounded by female foeticide)
- Gender inequity puts girls at greater risk than boys and affects many aspects of young women’s lives such as reduced opportunities for education, employment, and control over their own reproductive health.
- This in turn affects their health resulting from lack of awareness about nutrition, birth spacing, and contraception.
- Problem of exclusion (Ref: WHO):

| Scope of inclusive and equitable innovations are needed along with awareness and sensitization over the maternal health issue in India (Priority areas identified by Venture Center's Campaign Curator) |
- Some Central/state government majors are already in place.
- For example to access remote and geographically difficult terrains, Boat clinics – Assam and govt with a private organization. (Ref: IndiaGovernance)
- Janani Express Ambulance service (Ref: MoHFW-GoI)

- Technologies desirable for such majors:
- Handy, battery operated equipments
- Communication systems:
- Due to inadequate number of health workers, doctors can provide help in diagnosis or guidance in delivery using internet based multi-media technologies. Such technologies can also aid in integration of information from various resources.
- Affordable diagnostic/prognostic kits:
- Eclampsia: detection of proteins in urine, monitoring of blood pressure.
- Control of haemorrhage and family planning :
- Intra uterine devices : safer, inexpensive and reliable
- Affordable, quality nutrition that can be easily distributed/ Distribution systems:
- Deficiencies like Fe, Zn and Vitamin A can be ameliorated through such majors. These can be given as tablets or fortified in food: grains, fruits and vegetables sources.
